In today’s world, when we need something—like information, ideas, plans, or services—we usually start by asking search engines. Google, for example, handles a whopping 3.5 billion searches every day. Just as search engines have become a big part of our lives, they’ve also become essential for many businesses’ marketing strategies. Interestingly, 49% of marketers consider organic search to be the most profitable channel for Return on Investment (ROI).

Organic search is basically the standard, non-advertising results you get from search engines. Marketers leverage organic search through a process known as search engine optimization, or SEO.
Now, how can you make the most of search engines to boost your business? This comprehensive SEO guide will teach you all you need to know to rank higher on Google, increase your website traffic, and enhance your brand’s reputation.
Table of Contents
What does SEO stand for?
SEO stands for search engine optimization. Let’s simplify that in the context of your website.
- Search: This is what people do when they’re looking for an answer to a question or a product or service that fits their needs.
- Search engine: It’s a website (like Google or Bing) where someone can do that search.
- Search engine optimization: It’s what you do to make sure that the search engine connects that search with your website.

What is SEO?
Okay, you can tell me that RPA stands for robotic process automation, but that doesn’t really explain what RPA is.
So, what is search engine optimization?
A formal definition of SEO:
Search engine optimization is a combination of technical and content practices that aim to align a website page with a search engine’s ranking algorithm. This makes it easy to find, crawl, index, and appear in the SERP (Search Engine Results Page) for relevant queries.
A simpler definition of SEO:
SEO involves improving your website’s structure and content so that people searching for what you offer can discover your pages through search engines.
The simplest definition of SEO:
SEO is what you do to rank higher on Google and get more traffic to your site.
Yes, Google is just one search engine among many. There’s Bing, directory search engines, and even Instagram functions as a search engine. However, since Google captures 92% of the market share, for the purposes of this post, the terms “Google” and “search engine” are pretty much interchangeable.

Benefits & Importance of SEO
People are searching for all sorts of things, both loosely and directly linked to your business. These are chances to connect with them, address their questions, solve issues, and become a reliable resource.
Here’s what optimizing your site for search engines can bring:
- More website traffic: Optimizing for search engines means more visitors, increasing brand awareness.
- More customers: To optimize, your site needs to target keywords your ideal customers are searching, bringing in more relevant traffic.
- Better reputation: Ranking higher on Google instantly builds credibility. If Google trusts you, people trust you.
- Higher ROI: Investing in your website and marketing campaigns leading to it pays off with a top-performing site, making your investment worthwhile.
So, whether you aim for more brand awareness, online visibility, leads, sales, or loyal customers, SEO is the solution.
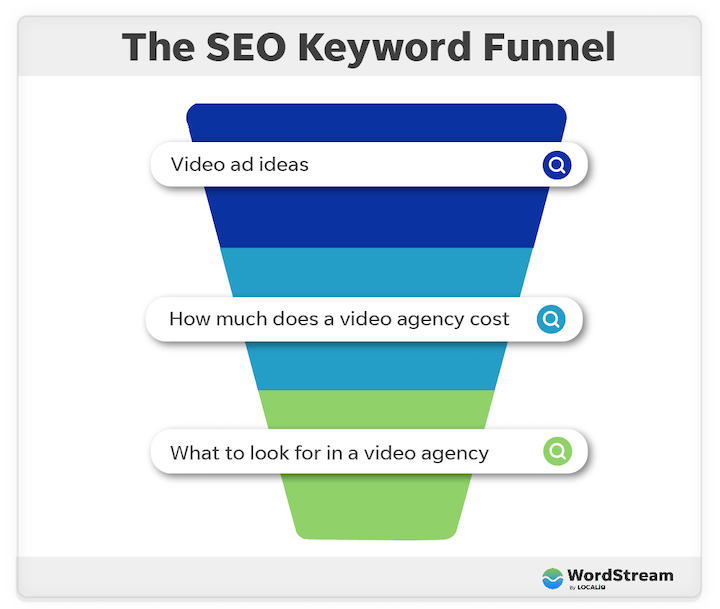
Types of SEO
Google and other search engines consider various factors when ranking content, making SEO a multi-faceted approach. The fundamental three types of SEO are on-page, off-page, and technical SEO:
- On-page SEO: This involves optimizing the quality and structure of the content on a page. Key players here include content quality, keywords, and HTML tags.
- Off-page SEO: It revolves around getting other sites and pages on your site to link to the page you want to optimize. Backlinks, internal linking, and reputation play crucial roles in off-page SEO.
- Technical SEO: This type focuses on enhancing your site’s overall performance on search engines. Site security (SSL certificates), user experience (UX), and site structure are key components.
These three types of SEO are applicable not only to websites and blogs but also to three subtypes of SEO:
- Local SEO: This aims to boost your business’s ranking on Google Maps and local results in the SERP. Priorities here include reviews, listings, and optimizing your Google Business profile.
- Image SEO: It combines on-page and technical strategies to make images on your website pages rank in Google image search.
- Video SEO: This involves a blend of on-page, technical, and off-page strategies to rank your videos in YouTube or Google video results.
While all three subtypes require aspects of the core types of SEO, they differ in the extent to which they rely on each core type.
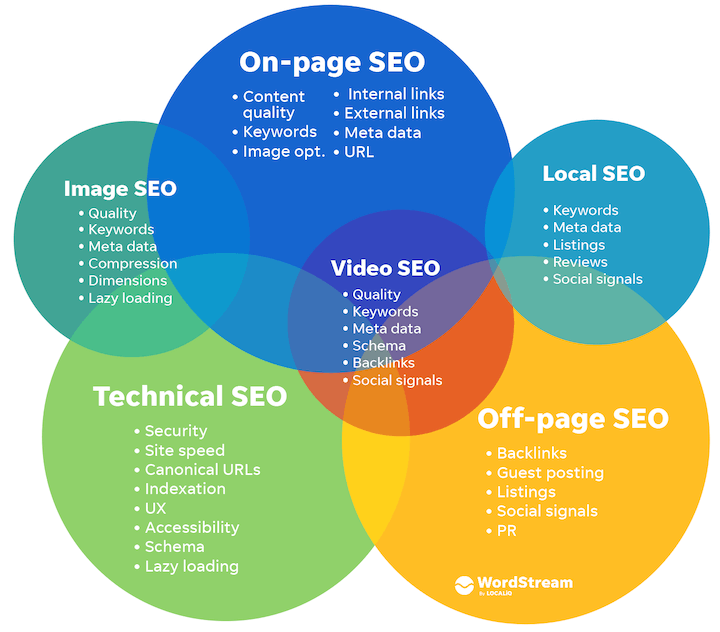
How does SEO work?
- So, how does Google decide which pages to show in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) for a specific query? And how does this impact traffic to your website? Let’s delve into how SEO operates.
- Google’s search crawlers are continuously scanning the web, collecting, categorizing, and storing the vast number of web pages in its index. When you search for something, and Google displays results, it’s drawing from its index, not directly from the web.
- Google utilizes a sophisticated formula, known as an algorithm, to arrange results based on various criteria (ranking factors, which we’ll discuss shortly). These criteria include the quality of content, its relevance to the search query, the website (domain) it belongs to, and more.
- The way people interact with these results further informs Google about whether each page is meeting the needs of users or not, and this information is also considered in the algorithm.

Simply put, SEO functions as a sophisticated feedback system. Its goal is to present the most precise, reliable, and pertinent results for any search, utilizing input from you, Google, and searchers. Your task is to generate content that aligns with Google’s expectations for experience, expertise, authority, and trust (E-E-A-T), meeting the needs of its searchers in the process.
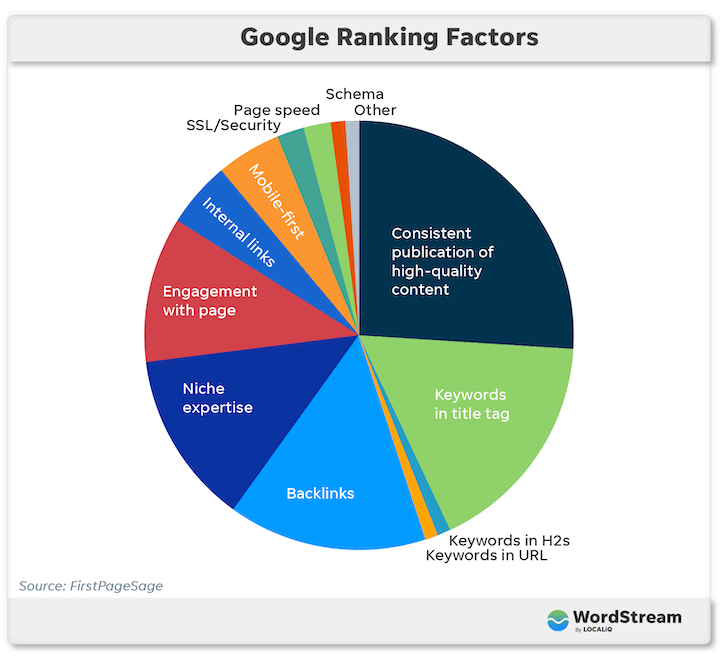
SEO ranking factors on Google
So, what exactly are these requirements? What defines quality, targeted, E-E-A-T-friendly, and SEO-optimized content? Well, there are numerous Google ranking factors, and Google is consistently refining its algorithm to enhance user experience.
However, focusing on these top 12 factors, as prioritized by FirstPageSage, is crucial:
- Consistent publication of high-quality content (26%)
- Keywords in meta title (17%)
- Backlinks (15%)
- Niche expertise (13%)
- User engagement (11%)
- Internal links (5%)
- Mobile-friendly/mobile-first (5%)
- Page speed (2%)
- Site security/SSL certificate (2%)
- Schema markup/structured data (1%)
- Keywords in URL (1%)
- Keywords in H1 (1%)
It’s important not to underestimate the factors towards the bottom of this list. While factors like unlinked mentions, social signals, domain history, outbound links, and site structure carry a 1% weight individually, considering there are over 200 Google ranking factors, these seemingly small elements collectively contribute to that 1%. In essence, even factors with a 1% weight, like keywords in the URL, play a significant role.
How to do SEO: On-page optimization
Let’s now discuss the practical steps to implement SEO—how to enhance your website for these factors to achieve a higher Google ranking and attract more traffic. This involves a blend of on-page, off-page, and technical optimizations, so let’s organize the steps accordingly. Here are the steps for on-page optimization:
- Start with keyword research
- Create quality content targeting those keywords
- Place your keywords
- Optimize your titles
- Optimize your meta descriptions
- Include and optimize images
- Internal and external links
1. Start with keyword research
The initial phase of search engine optimization involves identifying the keywords you want to optimize for. These are the terms that your ideal website visitors are likely to enter into Google or other search engines. It’s essential to assign a distinct keyword cluster to each page on your site to avoid competition among them.
How to do keyword research for SEO
Here are the fundamental steps to discover the optimal keywords for your organic content:
- Create your seed list: List the words and phrases your ideal customers use when searching on Google. Consider their interests, desires, pain points, and goals, focusing on the language they use rather than industry jargon.
- Use a keyword research tool: Employ keyword research tools to gather data on these keywords. These tools provide insights into terms you can realistically rank for and identify the best opportunities. Key metrics include:
- Search volume: The monthly frequency of searches for a specific term.
- Competition: The difficulty level in ranking for that keyword.
- Sort and prioritize: Organize the obtained terms and data in a spreadsheet. Group them into core themes and establish priorities. Aim for keywords with a search volume that provides decent reach but isn’t so high that the competition becomes too intense. It’s often better to rank on the first page for a less competitive keyword than to not rank at all for a highly competitive one.
2. Create quality content targeting those keywords
Your primary navigation pages, such as the homepage, about us, contact, products, and services, will target specific keywords. However, the majority of your keyword targeting will be through long-form content, typically in the form of blog posts. Quality SEO content possesses the following characteristics:
- Aligned with the keyword’s intent: Ensure your content addresses the information people are searching for when they use a particular keyword. Always perform a Google search for the keyword beforehand.
- Provides a good experience: Maintain a user-friendly experience by avoiding aggressive pop-ups, excessive calls-to-action (CTAs), or distracting elements. Utilize images effectively to illustrate concepts, and ensure your content loads quickly and correctly on all devices (more details on this in the technical SEO section).
- Reads naturally: Avoid keyword stuffing. Write in a conversational manner, addressing your audience like a human rather than a content writer solely focused on optimizing for search engines.
- In-depth: Google values substantial, unique content. Aim for 1,500-2,500 words that deliver accurate, current information, steering clear of thin, duplicate, or low-value pages.
- Organized: Use heading tags to signify the hierarchy of information on the page, aiding in the organization and structure of your content.
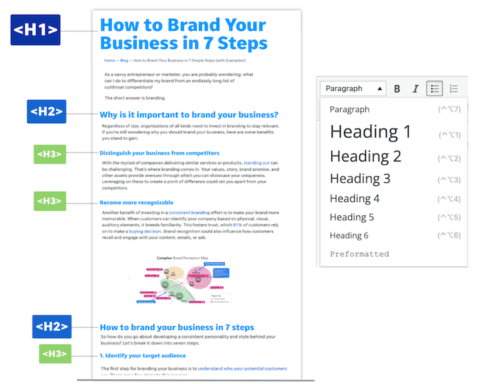
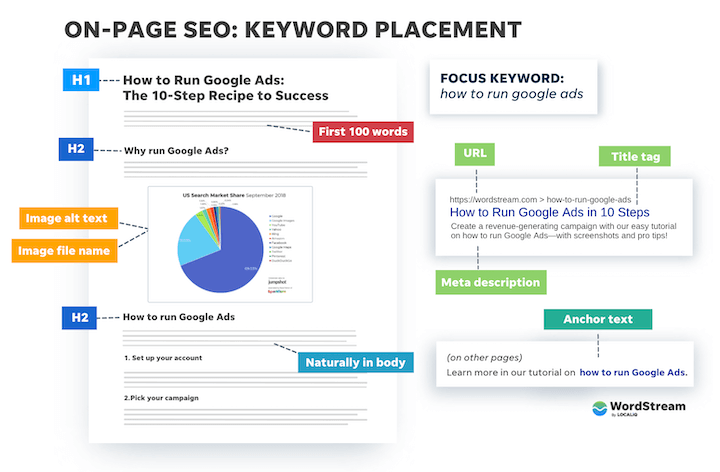
3. Place your keywords
Beyond naturally incorporating your keyword into the body of your content, strategically placing it in specific spots on the page signals to Google the focus of your content. This includes:
- SEO title (title tag): Craft a compelling title that includes your target keyword.
- Page title (H1 tag): Ensure your main page title, designated by the H1 tag, features your keyword.
- At least two H2 headings: Use H2 headings to structure your content and include your keyword in at least two of them.
- Image alt text: Provide descriptive alt text for images that incorporates your keyword.
- Image file name: Rename image files with a keyword-relevant name before uploading.
- Naturally in the body: Integrate your keyword naturally into the text to maintain a conversational tone.
- URL: Include your keyword in the URL structure, keeping it concise and relevant.
- Meta description: Write a concise and engaging meta description that includes your keyword.
4. Optimize your titles
For any page on your website, there are two titles to consider. The title tag is the title that appears on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) and holds significant weight for keyword impact. The H1 tag is the title visible when you click into the page. Whether these titles are the same depends on the specific page.
To optimize your titles, consider the following:
- Include the keyword: Add your keyword in a natural and compelling way. Incorporate related modifiers around the term if possible.
- Have only one H1 per page: Designate your main headline as the H1 tag. Use H2s to label the main sections of your content.
- Keep title tags to 55-60 characters: Google may display varying lengths (based on pixels, not character counts), so prioritize frontloading with the keyword.
- Indicate value: Clearly convey what users gain from the page. This influences their decision to click on it in the SERP or on your site and determines whether they continue reading.

5. Optimize your meta descriptions
The meta description is the brief description visible on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) below the title tag. Although Google may sometimes generate its own description, optimizing your meta description is crucial for SEO, as Google uses it to comprehend the page’s content during crawling.
To optimize your meta description, consider the following:
- Include the keyword and related keywords: If possible, incorporate the main keyword and related terms in a natural and compelling manner.
- Keep it short: Aim for an ideal meta description length of 155-165 characters.
- Make it compelling: Remember, appearing in search results is just the initial step. Encourage searchers to click by crafting a concise description, highlighting clear benefits, and including a call to action, similar to ad copy.
Here’s a real-world example of a meta description in search results:

6. Include and optimize images
Images play a crucial role in SEO optimization. They not only keep users engaged with your pages but also enhance the quality of information, offering opportunities to rank and generate traffic through image results. Additionally, with Google increasingly emphasizing visual elements in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP), optimizing images is more important than ever.
Here’s how to optimize images for SEO:
- File name: Save the file with the keyword, using dashes instead of spaces in the name.
- Add alt text: Alt text, or text alternative, is vital for Google to understand the image’s relevance to the keyword. It also ensures accessibility for screen readers and provides a description in case images break. Avoid keyword stuffing; describe the image as if you were explaining it to someone who can’t see it.
- Compress: Large images can slow down your site. Compress them to reduce file size and ensure proper sizing. Images wider than 1000px may not be necessary, but adjust according to your site’s needs.
7. Internal and external links
When optimizing blog posts for SEO, it’s essential to include both internal and external links.
- External links: Identify 1-3 pages related to the topic you’re focusing on, on other sites with high domain authority, and incorporate links to them in your post. This contributes to building trust with Google.
- Internal links: Within the content of your post, link to other relevant blog posts on your site. For example, as demonstrated in the last point, use phrases like “high domain authority” as anchor text. This practice provides Google with multiple pathways to any specific post, simplifying the overall crawling process of your site. The number of internal links depends on the post’s length and the available content for linking. Ensure the links are pertinent to the page and the anchor text used.
How to do SEO: Off-page optimization
All the steps mentioned earlier are focused on on-page SEO strategies. Conversely, off-page SEO involves actions taken outside the specific page you’re optimizing. This encompasses activities on other pages of your website, external websites, and even different platforms, all designed to enhance your page’s ranking. Here are some off-page SEO tactics:
8. Earn and reach out for backlinks
Backlinks, referring to links from other websites to yours, constitute the third most crucial Google ranking factor. Naturally, backlinks from high-credibility sites hold greater value than those from less credible ones. The quantity and quality of backlinks play a significant role in determining your ranking – the more high-quality backlinks, the higher your ranking.

To acquire more backlinks, consider these strategies:
- Create original, authentic content that is link-worthy.
- Proactively approach sites where a link to your content would be valuable.
- Engage in guest posting on relevant platforms.
- Seek PR coverage to increase visibility and attract backlinks.
9. Share your content on social media
Apart from including links to your homepage in social media profiles, regularly sharing your blog posts on these platforms is crucial. This not only generates referral traffic but also increases the visibility of your posts, enhancing the likelihood of acquiring backlinks. While social media activity isn’t a direct Google ranking factor, your engagement on these platforms and the audience’s interaction with your content send social signals to Google, influencing your overall ranking.
10. Build your brand reputation
When Google assesses the ranking of a specific page on your site, it doesn’t solely consider that single page. Instead, it takes a holistic view of your brand by examining various information across the web. This includes reviews, ratings, listings, awards, and even unlinked brand mentions. Therefore, cultivating your brand reputation by optimizing listings, garnering positive press, and encouraging reviews is crucial for SEO. While many of these efforts fall under the domain of local SEO, there are also numerous brand-building strategies that are applicable to businesses operating in non-brick-and-mortar settings.
How to do SEO: Technical optimizations
Technical SEO optimizations are conducted on the backend of your website to ensure it aligns with Google’s site security standards and enhances the user experience. These optimizations also aim to facilitate Google’s efficient functioning on your site. Here are some key technical optimizations to address:
- Page speed: Optimize the code behind your website content and the loading sequence to enhance page speed. Implement techniques like lazy loading and other optimizations.
- Security: Ensure your site uses HTTPS for secure communication rather than HTTP.
- Mobile-first: Simply being mobile-friendly is no longer sufficient. Given that Google now prioritizes mobile-first indexing, your site must be fully responsive to mobile devices.
- Core Web Vitals: Focus on three metrics (Core Web Vitals) that quantify the user experience with your page. Learn how to enhance your Core Web Vitals for improved performance.
- URL structure: Adopt an organized site structure, such as using /blog, /landing page, /product buckets. This structure makes it easier for Google to crawl your site, aids user navigation, and allows you to segment data effectively.
- Site architecture: Aim for a user to access any page on your site within three clicks or less. Internal linking plays a crucial role in achieving this goal.

- Canonical URLs: Canonical URLs play a significant role in managing duplicate pages. The canonical URL is the one you designate to represent a set of duplicate pages. Although Google attempts to identify the canonical URL for duplicates, you can explicitly convey this information to Google using canonical tags or 301 redirects. For instance:
- http://no1seocompanytoronto.com
- http://no1seocompanytoronto.com/
- https://www.no1seocompanytoronto.com
- https://www.no1seocompanytoronto.com/
All redirect to the designated canonical URL:
- https://www.no1seocompanytoronto.com
- Crawlability/indexability: Ensuring crawlability and indexability is vital. Your sitemap and robots.txt collectively communicate to Google which parts of your site should or shouldn’t be crawled and indexed.
- Schema markup: Implementing schema markup aids Google (and other search engines) in comprehending the types of content on your site.

This enables the display of rich results when applicable. For example, sitelink schema can provide more space on the SERP, while review schema enhances appeal.

Various schema types cater to different businesses. Further insights on schema and markup can be found in our comprehensive guide to schema for SEO.
SEO tools
Effective search engine optimization relies on data, and to gather data, you need tools. Fortunately, many of these tools are free, and they play a crucial role in optimizing your SEO strategy. Here are some of the best tools for an optimal SEO approach:
- Google Analytics: The gold standard for website traffic analytics, providing a wide array of free metrics. Measure performance metrics such as traffic, time on page, engagement, and more.
- Google Search Console (GSC): Essential for content-focused and technical SEO. GSC offers valuable data not fully available in Google Analytics, including Core Web Vitals, detailed query analyses, indexing insights, and more.
- Keyword research tools: Utilize these tools to find realistic keywords based on search volume and competition. Check out a roundup of the best paid and free keyword research tools to discover the right fit for your needs.
- SEO software: For in-depth SEO metrics like backlinks, competitive information, and advanced keyword data, consider using paid SEO tools such as Ahrefs, Moz Pro, Screaming Frog, SEMrush, etc. Some of these tools may offer free trial versions or free services for a limited number of links.
- Website graders: These tools simplify SEO and provide guidance, offering a user-friendly alternative to more complex tools.
SEO strategies and best practices
Let’s conclude with some SEO strategies, best practices, and tips to maximize your efforts:
- Always search the keyword: Users may not be searching for what you think they are. Verify keyword intent by searching the keywords you’re targeting to ensure alignment.
- Be patient: SEO is a gradual process, often taking months before results become evident. Stay committed, as the benefits compound over time. Don’t give up prematurely.
- Focus on quality: Google’s algorithm evolves, but its ultimate goal is to showcase the best content. Consistently create useful and trustworthy content as the primary SEO strategy.
- Maintain your content: While continuous publication of quality content is vital, don’t neglect older content. Regularly update evergreen pages to preserve their SEO value, ensuring consistent traffic growth.
- Track and measure: Regularly report on traffic and site data to identify popular topics, address issues, and set goals for sustained traffic growth. Monitoring metrics helps refine your SEO approach over time.
